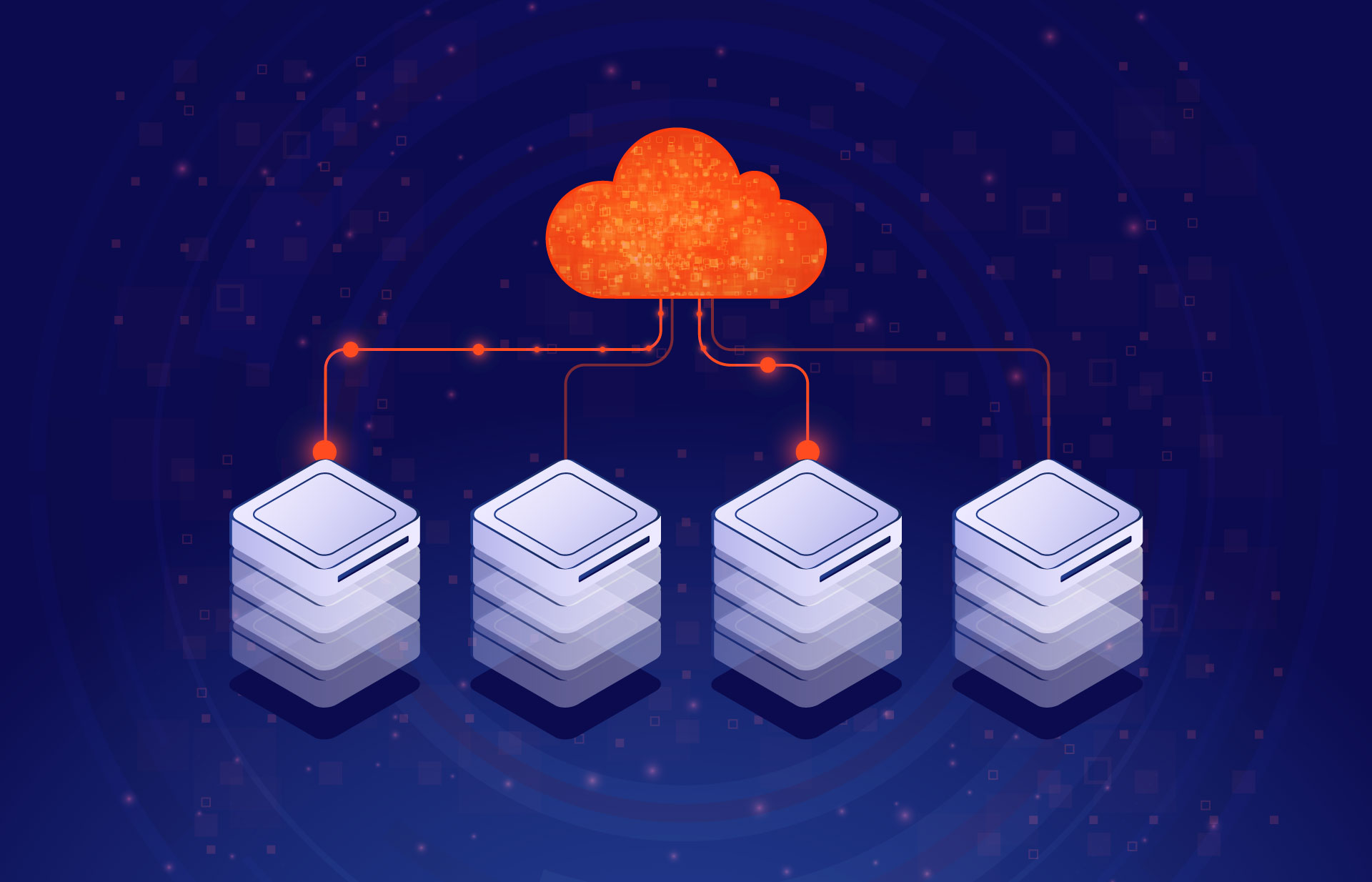
Nowadays, cloud computing provides larger possibilities for storing and accessing data than just simple computing. While your local storage is very vulnerable in terms of physical damages and is pinned to one place, with cloud technologies you can access your data and applications from anywhere around the world and be sure your software is safe and sound.
There are three main types of clouds: private, public, and hybrid.
Public clouds
Public clouds provide services to general public that can be accessed by anybody via the Internet. The infrastructure is owned and operated by third-party cloud services providers. All customers of public clouds share the same infrastructure (yet still having individual access to their data) and have access to scalable software environment. Public cloud is a cost-effective yet smart solution for running your virtual machines and storing your data. Examples of public clouds include Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM’s Blue Cloud, Google Cloud Platform, Windows Azure Services.
Conversely, a private cloud is designed to provide the environment solely for your organization and even though you are fully responsible for managing your data, at the same time you have absolute control over your environment and are ready to unpredictable business twists including workloads, security concerns, uptime requirements or management demands. Setting up private cloud architecture is a win-win decision for an organization with complex software infrastructure.

Obviously, hybrid cloud offers a combination of private and public cloud features, that gives customers the ability to choose the required options from both the public and private cloud environment. For example, sensitive data can be kept inside the organization’s private cloud and other services can be hosted in a public cloud, such as web-based email services. In such scenario, the organization itself manages and controls the private cloud, while the public cloud is operated and managed by the public cloud provider. Hybrid clouds are provided by AWS, Rackspace, Windows Azure, etc.
Private clouds have become extremely popular in the last years. By 2015, private cloud enterprise servers are projected to reach a revenue of $5,881,900,000. The benefits of deploying a private cloud can strongly affect the way businesses produce and consume IT services. Setting up a private cloud provides agility, security, customization and amazing performance of your apps. It is also easily scalable, flexible and reliable Extra storage and compute nodes can often simply be plugged into the system. You can start with small cloud and scale up as needed. You can begin with a few (two or three) servers and when your app needs more and more storage or cloud services you can add some more. A great security is ensured thanks to complete control over security parameters. You can also highly customize the whole environment, that ensures a better performance of your software and gives you more control over your infrastructure.
Private Cloud Platforms
Here at YourServerAdmin we’ve been working with such cloud platforms as Apache CloudStack and OpenStack. These platforms help us to deploy and manage large networks of VMs and assure high availability and scalability for a private cloud.
CloudStack is an out of the box solution. In the nutshell, it includes the entire “stack” of features most organizations want to have for their clouds including compute orchestration, Network-as-a-Service, user and account management, a full and open native API, resource accounting, and an excellent UI. OpenStack is one of the most popular open source cloud operating options today. This platform supports a wide range of software and hardware due to its open source nature. It also has the ability to manage compute, storage and networking and deploy them easily. There is number of differences between these two frameworks, you can read more about them HERE.
OUR SOLUTIONS
Private Cloud Management
Private Cloud Management requires software tools to help create a virtualized pool of on-demand self-services, as well as handle security, resource allocation, tracking, and billing. Different cloud management tools have their own feature sets. Those features encompass management across multiple clouds, configuration and monitoring third-party tools, dashboards and reports for detailed information about resource consumption, controlled access to resources to avoid over-usage or unauthorized access, and many others. The examples of such tools are Cloudability, Cloudyn, RightScale, IBM cloud management, and others.
The bottom line is that a private cloud provides an ability to integrate with all areas of your business. Security, performance, scalability, reliability, and availability are important areas to thoroughly consider setting up a private cloud for your company’s online business. If you are in doubts, you can always CONTACT US and we’ll discuss with you all the details of your project and offer the best solution for your project.